Physics
What's a solar eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the earth and the sun, blocking the sun's light. This alignment causes the moon to cast a shadow on the earth, partially (Penumbra) or fully obscuring (Umbra) the sun from view in certain areas.
For explanation of when to wear eclipse glasses to protect your eyes see also the safety information (no. 2).
Different Types (and phases) of solar eclipses
1. Total Solar Eclipse
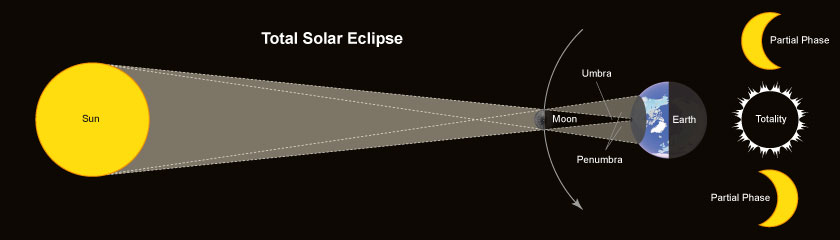
Schema of a Total Solar Eclipse
This happens when the moon is directly aligned with the sun and close enough to earth to appear equal or larger than the sun in the sky thus covering the sun's disk completely, as viewed from Earth. Before and after totality the moon covers the sun's disk partially (the partial phase of a total solar eclipse). During totality, which is visibly only along a narrow path on the earth's surface, the day momentarily becomes night, stars appear, and the sun's outer atmosphere, called the corona, becomes visible. Observers in the surrounding regions outside the path of totality will see a partial eclipse.
2. Annular Solar Eclipse
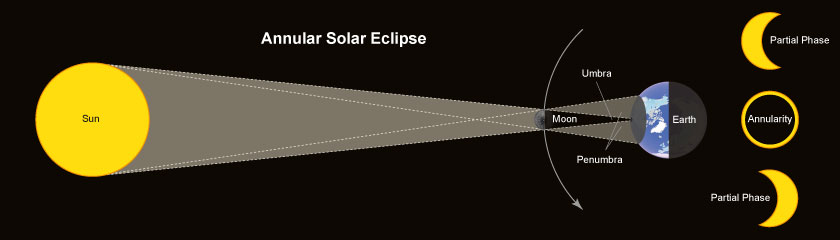
Schema of an Annular Solar Eclipse
This takes place when the moon is directly aligned with the sun but is a bit too far from earth to completely cover the sun's disk, as viewed from Earth. As a result, instead of totality, only an annular eclipse will happen, where a ring of the sun's outer edges, known as the ring of fire remains visible around the moon. and after annularity the moon covers the sun's disk partially (the partial phase of a annular solar eclipse). Observers in the surrounding regions outside the path of annularity will see a partial eclipse.
3. Partial Solar Eclipse
It occurs when only a portion of the sun's disk is obscured by the moon up to maximum degree of coverage. This happens when the alignment is not perfectly straight, so that the moon only covers a part of the sun's disk and passes either above or below the sun's disk. So in this case there is no 100% coverage and no path of totality nor annularity hits earth.

